Interesting and fun facts about the Colosseum for kids and curious adults: Colosseum facts to get ready for a visit to the Rome Colosseum with children and learn essential and cures facts about this wonder!
The Colosseum is the most recognizable of all Rome landmarks and one of the symbols of the city.
It is the biggest Roman amphitheater in the world and a building that never fails to capture the attention of children especially, who are likely to have seen in history books, cartoons, movies and videogames.
The Colosseum is full of interesting facts and stories and these are our favorites!
Going to Rome but hoping to skip expensive tours? I can help! My Ebook ‘Best of Rome with kids’ is all you need to plan a first trip to Rome with children and get the confidence and info you need to explore on your own, while still learning about the city and its wonders! Get it on Amazon!
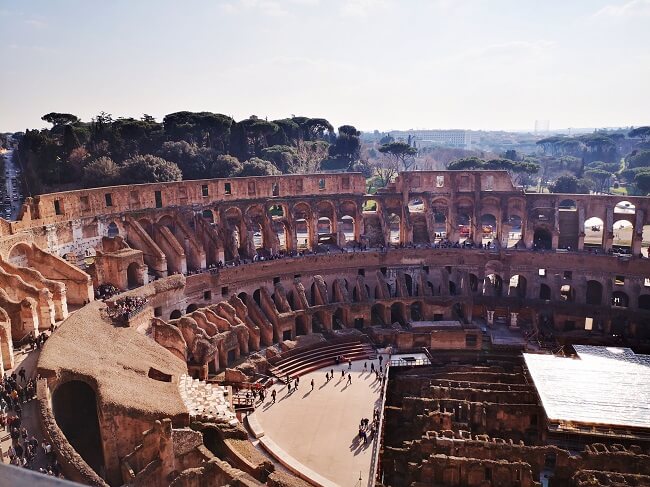

If you are planning a visit to Rome with kids, you can find here >>> our complete family guide to Rome.
Fun and interesting facts about the Colosseum for kids
I am a Rome mama and also an Ancient Rome history graduate from the University of Rome.
So, I feel I am very well equipped to give you facts about the Colosseum that are accurate, based on the historic and archaeological evidence we have right now, and that are intesresting for kids!
I recommend you use these facts to get them ready for the visit or to help you during the visit itself if going without a tour!
If you are in Rome and want to visit, these are the best tickets and tours to get!
What is the Colosseum
The Colosseum is a large ancient Roman amphitheater, used in ancient Roman times as a theater for live performances and gladiator fights.
It is a huge building, the biggest amphitheater in the Roman world.
The Colosseum has an oval shape, just like the one of the stadiums and arenas we have today. This is not by chance!
The Colosseum had the exact same roles that a stadium has today: it would host shows on a central stage and would have seats for spectators all around it.
How old is the Colosseum?
The Colosseum was built in the I century AD, under Emperors of the Flavian family: Vespasian, Titus and Domitian.
Vespasian started the built in 75AD, Titus finishes it and inaugurated the theater in 80AD and Domitian put finishing touches to it.
So the Colosseum is almost 2000 years old!
Because the Emperors’ surname was ‘Favian’ (Or Flavii, in Latin), the official name of the Colosseum is Flavian Amphitheater:
- Flavian = made by the Flavii emperors
- Amphitheater = oval shape theater
‘Colosseum’ is actually just a nickname!
When this area belonged to Nero, it hosted a large pond but also a very tall statue of Nero, so big that people referred to it as ‘The Colossus’.
When the Domus got destroyed, the statue was repurposed to represent the Sun God but stayed in place and became a landmark people started using to meet or make an appointment.
Imagine the chats: let’s to go to the games together, well shall me meet? Let’s meet at the Colossus!
This type of interaction, which is of course just an example, is what made the Colosseum acquire its nickname: even after the statue was gone, people would meet at the Colossus!
So the Colosseum is not called Colosseum because it is colossal, although it sure is big!
Fun fact: the metro station just beside it is called ‘Colosseo’, proving the ‘nickname’ really stuck! Colosseum is like most Romans call it now.
Why was the Colosseum built?
The Colosseum was built as a stadium.
It has the same shape as modern arenas (this is why they are called Coliseums!) and it was used by Roman emperors for centuries to offer shows and games to the Roman population.
Romans loved going to the stadium and the games. You can find here >>> the most popular shows and games in Ancient Rome.
Emperors used to host games as a way to show they were generous and popular and indeed, the shows at the Colosseum were always huge events that attracted large crowds.
The very first games happened in the Colosseum at its inauguration. When Titus held here the opening games, they lasted for 100 days that’s over 3 months!

Why was the Colosseum built here?
We don’t always as ourselves why a building is where it is; however, in the case of the Colosseum, its location has a very important meaning!
Before the Colosseum was built, the same area was occupied by the Palace of Emperor Nero: the Domus Aurea.
Nero, as you may know, thought very highly of himself and was keen to have a home that matched his high power and ambition. He therefore built a dome that was so big, with its building and gardens it occupied the whole of the hill beside the Colosseum and the entire area that is now occupied by the Colosseum itself! The Colosseum is where his garden pond used to be!
But Nero was not a popular person and when he died, Vespasian, his successor had an idea: the took the land that belonged to Nero and turned this private property into public land, on which he built a theater that would host games of everyone, for free!
It was a genius publicity stunt. By ‘giving back’ to the Romans this once private land, he positioned himself as a generous leader everyone looked up to.
Colosseum building techniques and materials
The Colosseum is made of large blocks travertine ( a type of white limestone) and tufo (a local stone), plastered and painted in, probably, bright colors.
These are the walls you still see as you enter the Colosseum and walk along the concentric corridors that lead to the seating area and the stage.
These walls were made more solid by the use of iron beams used as brackets.
These beams are not there anymore but we can still see ecactly where they were. Have a look at the walls around you: can you see holes in them?
These holes are where the beams used to be, before people stole them for cash in the Middle Ages!
The flooring of the seated areas was made of different materials: the more expensive seats had beautiful, precious floor. The rest…not so much!
As well as a stage and seats, the Colosseum had fresh water to drink and restrooms which we dan still see today!
Parts of the Colosseum
- Arena – the stage
- Cavea – the area of the Colosseum with the spectators’ seats.
- Underground area: storage, where the shows props and animals, where kept and the gladiators waited for their turn
- Attico: the very top ring of the Colosseum, probably originally a portico with columns
- Vomitoria: the Colosseum gates (see below!)
Facts about the Colosseum Arena
The arena is the Colosseum stage. It sits in the center of the amphitheater, it is flat and it is where the shows and battles took place.
The arena was covered in sand, which in latin is ‘arena’: the presence of sand helped cleaning up after the battles as it would absorb blood and fluids, inevitable during these intense fights.
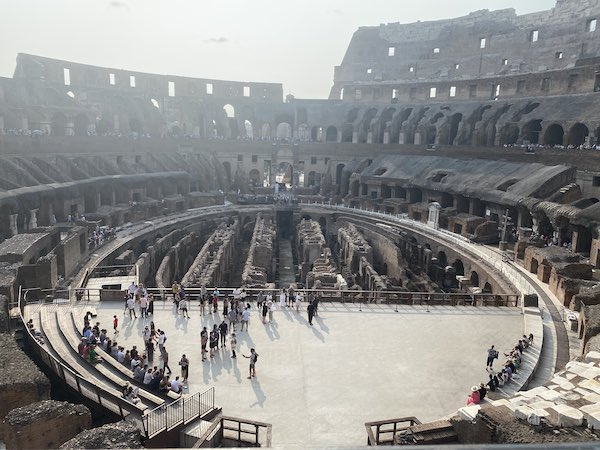

Facts about the Colosseum Cavea
The Cavea is the curved part of the Colosseum with the seats for the spectators.
The cavea was divided into 5 vertical sectors, with seats organised on the basis of the social status of the person who occupied them.
The Emperor has the best one, of course.
Important senators and vestals also had excellent ones, the so called Podium.
The rest of the population was organized so that the most important people has the best seats, while the poorer and least powerful and the further away ones.
The worse of all were for women and slaves and they were all the way up to the top, so they have to go up all those sites and could only see the stage from afar.
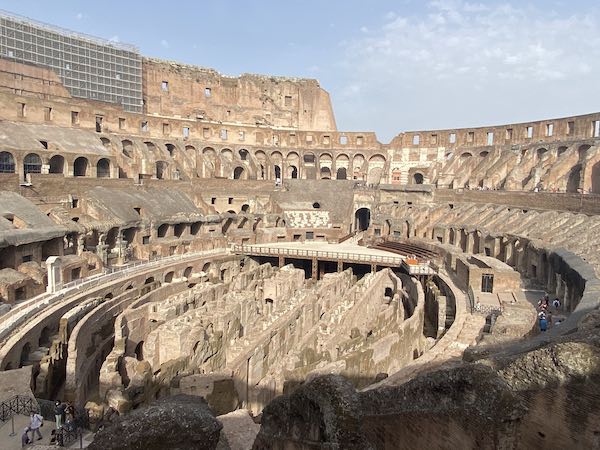

The Colosseum gates
The Colosseum was 150ft high, 550ft long, and 480ft wide and it seems it could hold up to 50,000 (50 thousand!) spectators.
To manage such a large number of spectators, the tickets where assigned so that each person had an assigned gate close to their sector.
Just like a modern stadium, each person would have a ticket that specified which entrance they should use to reach their seat quickly.
The Colosseum had 80 entrances that people used to enter and exit the theater quickly
The different entrances to the Colosseum were also a way to ensure quick exit. The gates had a special name: ‘vomitoria’.
Does this word make you think of vomit? You are right? It is because they allowed the crowds to get out fats as if the theater was ‘vomiting’ them out!
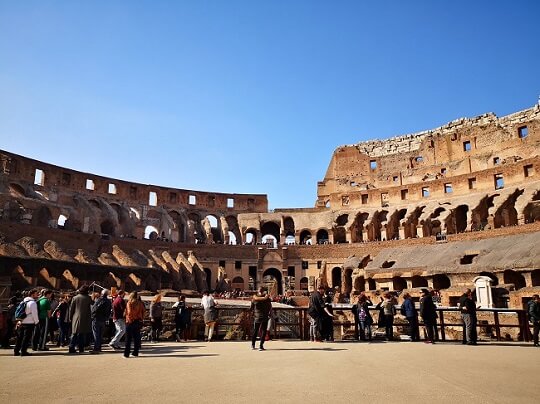

What types of shows happened in the Colosseum?
Several types of shows were performed in the colosseum including fights (gladiator vs gladiator or munera), gladiator vs animal fights (venationes).
During game days, other events also took place in the Colosseum such as capital executions.
The games where organized by an editor, who would put together the program an publicise it ahead of time to drum up interest. The editor would also offer the game, so that people would go for free (yes, tickets to the Colosseum gates were FREE in Ancient Rome!)
The ip editor was, of course, the emperor, who liked to show his generosity and gain popularity by sponsoring expensive and extravagant games.
Other editors were young magistrates who may have to sponsor games to gain visibility and prestige.
The games would see the participation of gladiators, especially famous ones who would draw the largest crowds.
The program, once finalized, was painted on walls in visible locations around the city, just like we now use posters to let people now about an event.
Gladiator fights were the main event of the day and usually held in the afternoon, to build up excitement.
You can learn here >>> all about Roman gladiators
In the morning, the other popular type of shows held in the Colosseum too place: the animal fights.
The Romans went to all lengths to secure exotic animals to impress the crows.
Among the others, they say the Colosseum hosted fights with elephants, bears, bulls, tigers and lions!
To ensure the maximum visual impact and surprise effect, the animals were kept under the stage, underground. There, they would wait in cages and then be placed of an elevator opetated by slaves, the would lift them all the way yp to the stage.
There is a replica of the lift in the Colosseum now: you can see it best if you visit the underground part.
Shows were one of the most popular pastimes in Ancient Rome and aways attracted large numbers of spectators.
According to ancient sources, the Colosseum was also equipped with a system that would flood its arena area and allow for battles between ships.
While this seems plausible to archaeologists, there are several reasons to believe that these battles, if ever happened, were not a common occurrence: it is possible only one ever took place, in occasion of the Colosseum’s inauguration.
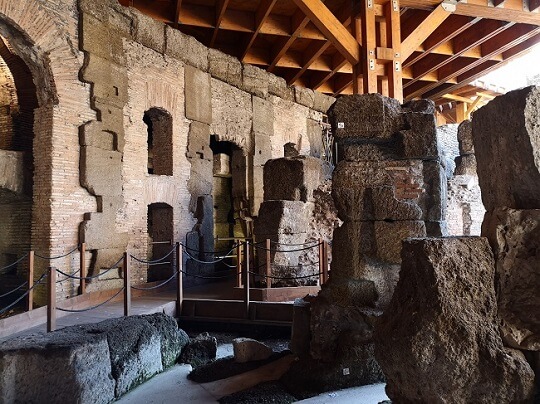

Facts about the Colosseum Underground area
the underground area of the Colosseum was the Colosseum backstage.
Here the game organisers kept all the theater props, the animals as they waited their turn, they would operate the animal lift. Here is it also where the gladiators would wait for their turn.
This area was below the stage and was dark and oppressive. Nowadays, to make it pleasant for visitors, they took off part of the arena floor, so when you are underground you actually see the sky and can breathe well.
But back in the day, imagine how dark and awful it must have e been!
Underground is also where you find a special corridor connecting the inside of the Colosseum to the nearby Gladiators’ hospital.
If a professional gladiator got injured, they’d quickly bring him to the hospital to cure him!
Need to know! Gladiators didn’t always fight to their death. In many cases, gladiators were professional athletes and the last thing anyone wanted was for them not to be able to fight anymore. So the idea was that they had to put on a fabulous fight show by stay well in shape to be able to keep performing: they had the best diets and best doctors, just like famous sportspeople now!

The last hunt in the Colosseum happened in 523 AD
The Golden era of the Colosseum games was the Roman Empire, however, hunts happened here up to 523AD, so after the fall of the Western Roman, Empire.
During Christian times (IV – VI century) only hunts happened here asChristian Emperors made gladiator games illegal.
From they moment on, the Colosseum went though slow but steady decline and, in the Middle Ages, it was abandoned.
It became full of unusual plants and flowers making it interesting for botanists more than historians.
This is why in many paintings you will see it abandoned and surrounded by overgrown vegetation and even grazing cattle!
For a long time used as a quarry: marble used to build St Peter’s Basilica famously cames from here!
The Colosseum Cross
Inside the Colosseum you will notice a very tall cross. For a long time, it was believed that the Colosseum was a place where Christians were killed, during prsetutions happening during the Pagan Roman empire.
However, there are no sources about this, no source actually mentions the Colosseum as a place of martyrdom.
However, the church in 1750 decided to honour the martyrs consecrating the Colosseum to them, by hand of Pope Benedict XIV. This is also the reason why, each Good Friday, the Pope’s way of the cross ends here!
I hope you enjoyed these facts about the Roman Colosseum and you can soon go visit!
If you do, make sure you read our tips for visiting the Colosseum with kids first and read about our experience visiting the Colosseum top tier and underground area, so you know what to expect.
Did you enjoy these facts about the Colosseum for kids? Save them on Pinterest!

This post was originally written in 2020 and has now been updated with recent photos and additional info (November 2023)